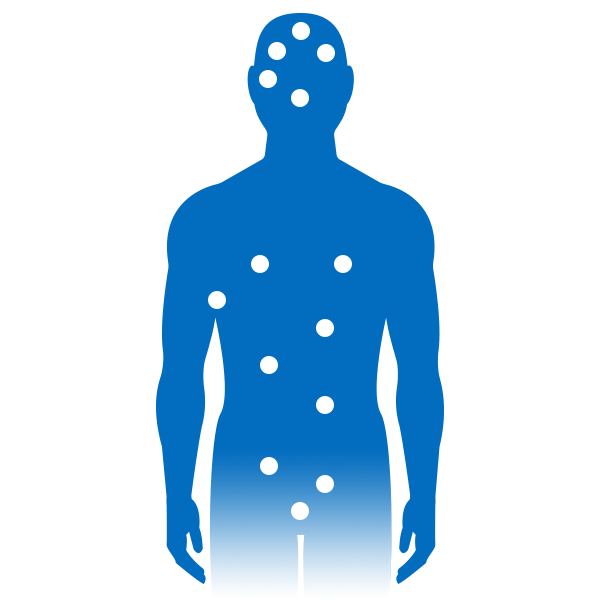




Alcohol can result in aggressive behaviour,
risk-taking and blackouts.
After having a drink, the immediate effects can be pleasant. People may feel happier, more relaxed or more outgoing around others.
Drinking more than recommended by the Low- Risk Alcohol Drinking Guidelines on any single occasion can result in people taking risks they normally wouldn't or acting more aggressively than usual. This can lead to getting into dangerous situations or saying and doing things they might later regret.
A quick rise in blood alcohol content can prevent the brain from forming memories resulting in a blackout - a permanent loss of memories for a specific period of time.

Functions like balance and vision are impaired leading to accidents.
Alcohol slows down certain functions the brain controls such as balance, muscle coordination, vision and the ability to react to unexpected events. This can increase the risk of injury from things like falls or car accidents.

Alcohol reduces the skin's ability to stay smooth and healthy.
When alcohol is consumed, it dehydrates the body - and that includes the skin which needs moisture to stay smooth and healthy.

Drinking has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.

Alcohol can cause unpleasant body odour as it's processed.
Though the liver processes most of the alcohol consumed, some of it leaves the body through breath, sweat and urine which can
cause unpleasant body odour.

Diseases like cirrhosis and hepatitis can occur with heavy drinking.
When the liver has to process large amounts of alcohol over time, its cells can be damaged. Over time, this can lead to serious medical
conditions such as fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Both hepatitis and cirrhosis can lead to premature death.

Drinking may cause diarrhea and is linked to bowel cancer.
Alcohol use can cause diarrhea and over time, has been linked to irritable bowel syndrome and an increased risk of bowel cancer.

Alcohol affects the body's ability to get a good night's sleep.
While alcohol may help with falling asleep, it does not help with getting a good night's sleep because it interferes with the deep sleep
cycle - the cycle needed to feel truly rested.

Heavy drinkers may experience depression, anxiety and relationship problems.
Because alcohol is a depressant, it may contribute to depression and anxiety in heavy drinkers.
When ongoing drinking affects relationships with family and friends or performance at work or school,
this is often a sign of alcohol problems.
High blood pressure and stroke could result from drinking.
Over time, drinking can cause high blood pressure, weaken heart muscles and increase the risk of stroke and irregular heartbeat.
There is some evidence that moderate drinkers have a somewhat lower risk of heart disease and stroke than those who do not drink or who
are heavy drinkers. It's thought that moderate drinking may increase HDL cholesterol levels (the "good" cholesterol), reduce the
incidence of heart attacks and provide other cardiovascular benefits.
For young people, there are no known health benefits from drinking alcohol. For this age group, drinking can actually interfere with normal growth and development.
The latest health guidelines are clear - no one should begin drinking or drink more frequently to gain potential health benefits.
Consider talking to your health care provider if you have any questions about the health benefits or risks of drinking.

Drinking can increase the risk of illnesses and infections.
Drinking can reduce the body's ability to fight infections. over time, drinking can increase the risk for getting serious infectious diseases such as tuberculosis. Drinking can also affect how some illnesses, like tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS, progress

Alcohol can cause vomiting and is linked to stomach cancer.
In the short-term, alcohol can cause nausea and vomiting. Alcohol use over time has been linked to a higher risk of stomach cancer.

Alcohol causes the body to release more fluid into the bladder.
Alcohol blocks the release of a hormone in your body that helps you retain water so when you drink, there are lower amounts of this
hormone in your body - meaning more liquid is released into your bladder.
That's why in the short term, drinking alcohol often means more bathroom breaks.

Drinking can reduce fertility and increase participation in high-risk sex.
For women, drinking can affect menstrual cycles and fertility in the long-term.
For men, drinking can lower testosterone levels in the long-term and negatively affect sexual performance both immediately and in
the long term.
Drinking affects judgment which may mean participating in high-risk sexual activity like unplanned sex, unprotected sex and even
unwanted sex. This may lead to regret and an increased risk of pregnancy and sexually transmitted infection.